Everything You Need to Know About the Circulatory System
Overview
What is the circulatory system?
Your centre and blood vessels make upwardly the circulatory system. The primary function of the circulatory organization is to provide oxygen, nutrients and hormones to muscles, tissues and organs throughout your body. Some other office of the circulatory system is to remove waste from cells and organs so your torso tin can dispose of it.
Your middle pumps claret to the trunk through a network of arteries and veins (claret vessels). Your circulatory organisation can also be divers every bit your cardiovascular organization. Cardio means heart, and vascular refers to blood vessels.
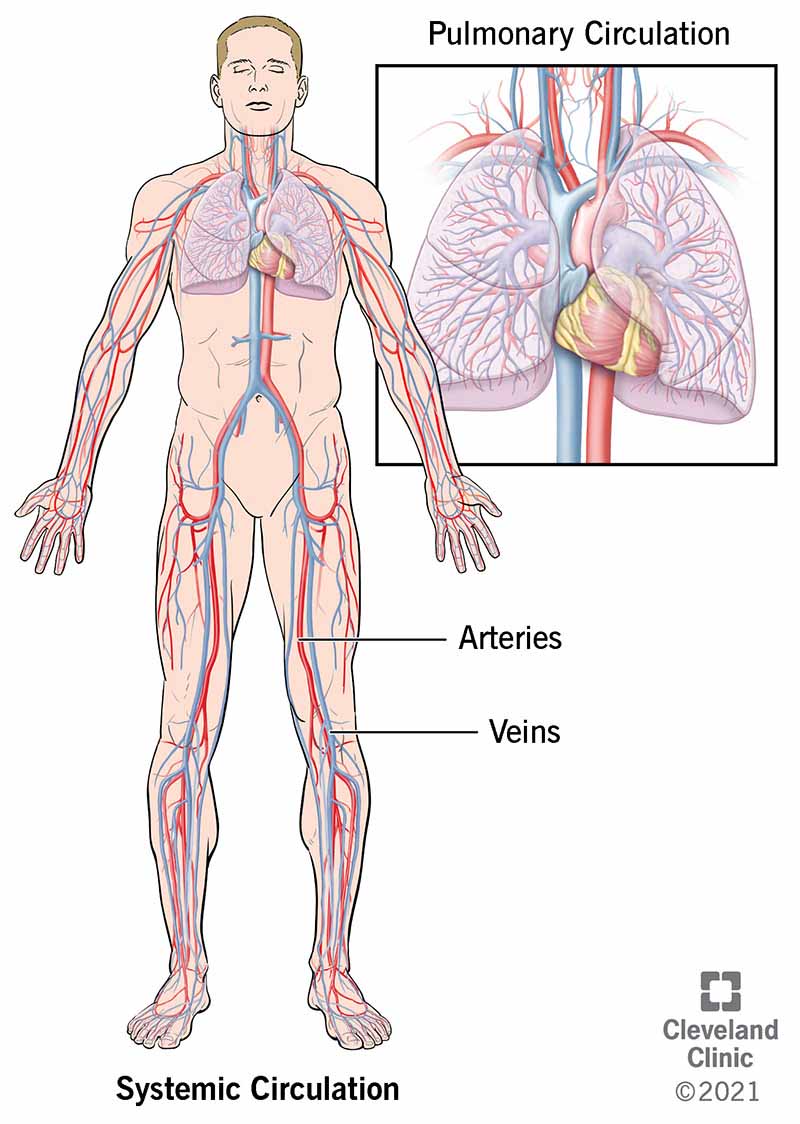
The circulatory system provides blood to all the trunk's tissues and then they can function.
Function
What does the circulatory system do?
The circulatory system's function is to move blood throughout the body. This blood circulation keeps organs, muscles and tissues good for you and working to keep you alive.
The circulatory system also helps your body go rid of waste material products. This waste includes:
- Carbon dioxide from respiration (animate).
- Other chemical byproducts from your organs.
- Waste from things you lot eat and drink.
How does the circulatory system work?
Your circulatory system functions with the help of blood vessels that include arteries, veins and capillaries. These blood vessels piece of work with your heart and lungs to continuously broadcast blood through your body. Hither's how:
- The eye'southward bottom right pumping bedchamber (right ventricle) sends blood that's low in oxygen (oxygen-poor blood) to the lungs. Blood travels through the pulmonary trunk (the main pulmonary artery).
- Blood cells pick upward oxygen in the lungs.
- Pulmonary veins carry the oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart's left atrium (upper heart sleeping room).
- The left atrium sends the oxygenated blood into the left ventricle (lower chamber). This muscular role of the centre pumps blood out to the body through the arteries.
- Equally it moves through your trunk and organs, claret collects and drops off nutrients, hormones and waste products.
- The veins carry deoxygenated blood and carbon dioxide back to the heart, which sends the blood to the lungs.
- Your lungs get rid of the carbon dioxide when yous exhale.
Anatomy
What are the circulatory arrangement parts?
The parts of your circulatory organisation are your:
- Heart, a muscular organ that pumps claret throughout your torso.
- Blood vessels, which include your arteries, veins and capillaries.
- Claret, made upward of red and white blood cells, plasma and platelets.
What are the circulatory system circuits?
Your circulatory system has three circuits. Claret circulates through your heart and through these circuits in a continuous design:
- The pulmonary excursion: This excursion carries claret without oxygen from the heart to the lungs. The pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood to the heart.
- The systemic excursion: In this circuit, blood with oxygen, nutrients and hormones travels from the center to the rest of the body. In the veins, the blood picks upward waste products as the body uses upwardly the oxygen, nutrients and hormones.
- The coronary circuit: Coronary refers to your center'southward arteries. This excursion provides the heart musculus with oxygenated claret. The coronary circuit then returns oxygen-poor blood to the middle'south correct upper sleeping accommodation (atrium) to send to the lungs for oxygen.
What are the types of blood vessels?
At that place are iii main types of claret vessels:
- Arteries: Arteries are thin, muscular tubes that carry oxygenated claret away from the heart and to every function of your body. The aorta is the trunk's largest artery. Information technology starts at the heart and travels up the chest (ascending aorta) then down into the tummy (descending aorta). The coronary arteries co-operative off the aorta, which then branch into smaller arteries (arterioles) as they get farther from your middle.
- Veins: These claret vessels return oxygen-depleted blood to the heart. Veins start small-scale (venules) and get larger every bit they approach your heart. Two cardinal veins deliver claret to your heart. The superior vena cava carries blood from the upper body (head and arms) to the middle. The junior vena cava brings claret up from the lower trunk (breadbasket, pelvis and legs) to the centre. Veins in the legs take valves to keep blood from flowing backward.
- Capillaries: These blood vessels connect very minor arteries (arterioles) and veins (venules). Capillaries have sparse walls that permit oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients and waste products to pass into and out of cells.
What are the circulatory arrangement organs?
Your heart is the merely circulatory system organ. Claret goes from the center to the lungs to get oxygen. The lungs are role of the respiratory arrangement. Your heart then pumps oxygenated blood through arteries to the rest of the body.
Conditions and Disorders
What conditions affect the circulatory system?
Many conditions can affect the health of your circulatory system, including:
- Aneurysms: Aneurysms occur when an avenue wall weakens and enlarges. The weak spot can burl as blood moves through the artery. The weak spot may tear, causing a life-threatening rupture. Aneurysms tin affect any artery, but aortic aneurysms, abdominal aortic aneurysms and brain aneurysms are the most common.
- High blood pressure: Your arteries work hard to circulate blood throughout the body. When the pressure level (forcefulness of blood against the blood vessel walls) gets too high, you develop high blood pressure. When the arteries become less rubberband (stretchy), less blood and oxygen reaches organs like the heart. High blood force per unit area puts y'all at take chances for cardiovascular disease, heart attacks and strokes.
- Plaque deposits: High cholesterol and diabetes can lead to fat and other substances collecting in the claret. These substances form deposits called plaques on artery walls. This condition is atherosclerosis, or narrowed or hardened arteries. Atherosclerosis increases the risk of blood clots and strokes, coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease (and other artery diseases), centre attacks and kidney disease.
- Venous disease: Venous diseases tend to affect veins in the lower torso. Problems like chronic venous insufficiency and varicose veins occur when blood tin't flow back to the heart and pools in leg veins. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a blood clot in the legs, can atomic number 82 to a life-threatening pulmonary embolism.
Care
How can I prevent circulatory arrangement bug?
These steps can protect the wellness of your circulatory system:
- Aim for at to the lowest degree 150 minutes of concrete activity every calendar week.
- Eat a heart-salubrious diet rich in vegetables and cobweb and low in saturated fats and candy foods. Consider a Mediterranean-style diets or plant-based diet, as they appear to be the most heart healthy.
- Find healthy means to ease stress.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Manage conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure and loftier cholesterol.
- Get help to quit smoking.
Ofttimes Asked Questions
How big is the circulatory organization?
Your body has more than sixty,000 miles of blood vessels that broadcast near 1.5 gallons of blood every 24-hour interval.
What is reddish blood and blue blood?
All blood is red. Hemoglobin, an iron-rich protein in cherry blood cells, mixes with oxygen to requite blood its ruddy colour. Blood that's rich in oxygen is known as ruddy blood.
Your veins comport oxygen-poor claret. This is sometimes called bluish blood because your veins can look blue underneath the skin. The blood is actually red, merely the low oxygen levels give veins a bluish hue.
Do arteries always carry oxygenated blood?
For the most role, yes. The exceptions are pulmonary arteries and veins. Pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated claret to the lungs. Pulmonary veins return the oxygenated blood to the middle.
A note from Cleveland Dispensary
Your circulatory arrangement plays a critical role in keeping you alive. Blood vessels carry claret to the lungs for oxygen. So your eye pumps oxygen-rich blood through arteries to the residual of the torso. Your veins aid your body get rid of waste material products. Conditions similar high blood pressure level, high cholesterol and atherosclerosis can touch on the health of your circulatory organization. If yous have ane of these weather, talk to your healthcare provider near steps y'all can accept to protect your cardiovascular health.
Source: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21775-circulatory-system
0 Response to "Everything You Need to Know About the Circulatory System"
Post a Comment